The SMC Staging Service in Fargate - Overview & Tutorial
Context Diagram
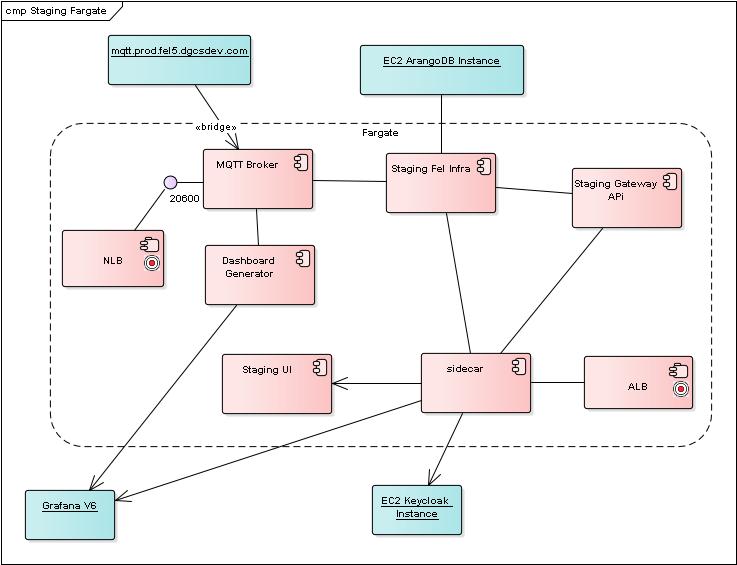
The diagram shows the components that are created in Fargate by the staging deployment and those EC2 components from the existing production service that are used by the staging stack. The EC2 components are shown in blue.
EC2 Components
MQTT Broker
The current deployment uses a single infra-api component to surface the FEL production infrastructure. Signals from this infrastructure are currently collected by the mqtt.prod.fel5.dgcsdev.com broker. To avoid any changes to production staging signals will be collected from this broker.
Graph Database
Whilst it is possible to create an instance of ArangoDB in fargate using the existing SMC Fargate framework the initial requirements were to make use of the EC2 instance of ArangoDB that is used in production
Fargate Components
Elastic Load Balancer
The Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) is used by all MQTT instances in Fargate. It provides the following capabilities:-
-
Exposure of TCP connections on port numbers associated with the mqtt-gate DNS entry
-
Management of certificates for non-HTTP(S) connections
-
Termination of SSL connections
-
Keep-alive for MQTT briokers and restart of failed processes
Application Load Balancer
The Application Load Balancer (ALB) is used by all HTTP(S) internet-facing components in Fargate it is responsible for:-
-
Termination and re-establishment of SSL connections
-
Certificate Management
-
Host routing
-
Keep-alive and restart of Fargate tasks
MQTT Broker
Staging runs an MQTT broker that bridges from the production broker in EC2. The reason for this is that it reduces the load on the production broker and provides a single point within the Fargate infrastructure to retrieve signals
Dashboard Generator
There is no EC2 dashboard generator for the FEL infrastructure in staging so a Fargate instance is created that retrieves signals from the Fargate MQTT Broker and creates dashboards in the EC2 Grafana V6 instance.
Staging FEL Infra
An instance of the infra-api is created in Fargate it accesses the Fargate MQTT Broker but also uses the ArangoDB database in EC2
Staging Gateway API
A single Gateway API is created in Fargate to manage the staging infras (so far only one n this stack). It also uses the EC2 instance of ArangoDB so that it is consistent with the infra if fronts.
Defining The Deployment
Our Fargate deployments all use Infrastructure As Code definitions. This means that we do not create server instances, install Operating Systems & software, perform configuration etc. Instead, we create a code definition of what we want to exist and then have the infrastructure create that declared end-state.
The declaration for the staging deployment is illustrated below:-
/**
* STAGING DEPLOYMENT
* @Public
*/
const staging: Deployment = {
id: 'staging', // Carried through to Dashboard agent id, logging streams and sidecar
// return for /deploymentId
version: '0.0.1', // Sidecar returns this value for /version
cluster: 'staging', // Fargate cluster to deploy to - intent is each deployment has a different cluster
azs:['eu-west-1a'], // Availability zone(s) to spread the deployment across
deployLevel: 'test', // Passed through to infra-api and gateway instances
nodeEnv: 'development', // Execution mode for NodeJs. The interpreter will make some optimisations
// If this is set to "production". Also used by infra-api and gateway
organisation: 'staging', // Organisation passed to Gateway
smcAlerts: 'false', // Passed to dashboard, infra-apis and writers
publicAccess: 'true', // Passed to gateways and infra-apis. Note that both are instantiated on private
// IP addresses notwithstanding the value of this parameter
infraApis: [
stagingFelInfra // Single infra-api for FEL infrastructure
],
gateways: [
stagingGateway // Single Gateway
],
graphDatabase: stagingGraphDatabase,
// Points to "legacy" ArangoDB instance in EC2
dashboards: {
serviceId: 'dashboard_generator',
// Used to create the service name for the agent
dashboards: [
stagingFelDashboard // Single dashboard generator for Fel infrastructure
] // Dashboards created in 'Legacy' Grafana instance
},
grafana: { // Grafana instance to use in the case of staging this
// is the EC2 hosted instance of Grafana 6
externalHost: 'ui.cloud.smartermicrogrid.com',
protocol: 'https',
port: 443,
baseUrl: '/grafana',
ignoreSSL: 'true', // Allow self-signed certificates
apiKeyHandle: 'Staging-SMC-FEL-Grafana-Key'
},
brokers: [ // Single broker defined in staging bridges from Prod Fel
felBroker
],
uis: [
stagingUi // Latest UI version
],
sidecars: [
stagingSidecar // Sidecar attached to supermicrogrid.com address
]
}Deployment Header
The first set of values to the Deployment constitute the deployment header. They fix several key elements that describe how the various tasks that make up the deployment will be committed to infrastructure.
Variable |
Purpose |
id |
The id parameter is used to collect together elements of a deployment under the same name. The dashboard generators, the logging streams, the URL routing will all be tied together with this id |
version |
The version parameter represents a version identifier for the whole deployment it will be returned in requests to /version - see for example |
cluster |
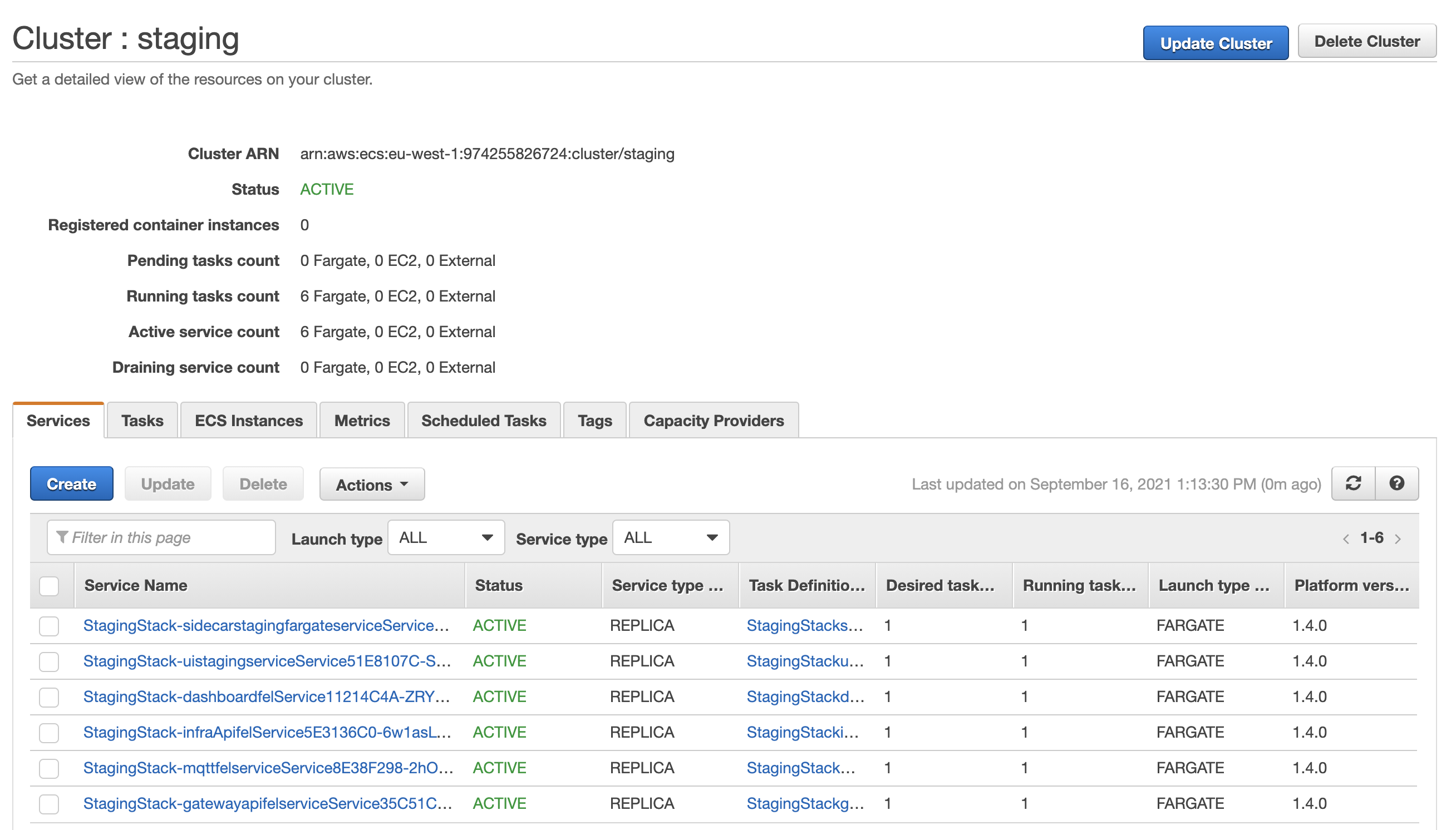
The Fargate cluster into which all the components described by the deployment should be installed. The image below illustrates the current state of the staging cluster. |
azs |
A list of AWS availability zones (AZs) across which the cluster should be deployed in this case we have selected a single AZ |
deployLevel |
Used as a discriminator in the Git path to select policy definitions |
nodeEnv |
Overrides the NodeJS |
organisation |
Deprecated?? |
smcAlerts |
Send E-mail alerts for errors raised if set |
publicAccess |
Allow guest access to the infrastructure if set |
The remainder of the deployment descriptor identifies the tasks and connections that are required to create the components we described earlier. Post deployment our staging cluster would look something like:-
INFRA Apis
The deployment above contains a single definition for an Infra-API. The list of infras has a single element stagingFelInfra. To understand the details we need to look at the definition for this code element
/**
* @public
* FEL Infra API
*/
export const stagingFelInfra:InfraAPI = {
id: 'fel', // Sidecar will build rules for URL /api/<id> to access the infra
agentId: 'fel_fargate', // Used as the MQTT agent Id when enrolling with a broker
agentName: 'fel_fargate_infra',
// Docker image to deploy from the Elastic Container Registry
image: 'dgcsdev/edge:infra-api-18.1.7.x86',
// Dashboard generator for this infra
dashboard: stagingFelDashboard,
// Reference to ArangoDB Database to use in this case EC2 instance
graphDatabase: stagingGraphDatabase,
// Organisation codes in Grafana
autoOrgId:Organisation.Staging_FEL_Auto,
customOrgId:Organisation.Staging_FEL_Custom,
// URL for V6 Grafana in EC2
grafanaUrl: 'https://ui.cloud.smartermicrogrid.com/',
// We use fixed broker client IDs in Fargate because the
// frequent changes in IP address otherwise put heavy loads
// on the broker
brokerClientId: 'fel-infra-client@infra-fel.fargate.smc.local',
broker: fel5Broker, // MQTT Broker in Fargate
noAuth: 'true',
port:80,
healthCheckPort: 8038, // Keep alive port
authKey: 'Staging-SMC-Fel-Infra-Auth-Key',
keys: defaultGatewayKeys
}